5G is on everyone’s lips. But what is behind this abbreviation? When will the 5G network exist and what are the opportunities and risks?
The essentials in brief:
5G is the successor to 4G (LTE) and describes the 5th generation of mobile communications.
The 5G standard enables data transmission up to 10 times faster than LTE and thus communication in real-time.
5G has already been available in some cities since July 2019.
The new mobile communications standard is intended to support the digitization of many areas of life.
Table of Contents
What is 5G technology?
5G is the next generation of mobile broadband that will eventually replace, or at least increase, your 4G LTE connection. With 5G, upload and download speeds will be exponentially faster. Latency, or the time it takes for devices to communicate with wireless networks, will also drop dramatically.
5G networks are touted as promising an exponential leap in the amount and speed of wireless data, enabling advancements in autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, connected health, and more as sensors and servers instantly communicate.
To get that speed, 5G uses higher frequencies than current networks. The trade-off with higher frequencies is that their signals don’t travel that far and are easily blocked by buildings. This means that more antennas will be needed to connect to the phones.
It worries some people, who were already frightened by the giant antennas placed on top of towers and buildings. 5G networks will use many smaller antennas closer to people, such as on top of streetlights, which could expose people to even more radio waves.
Features of 5G technology
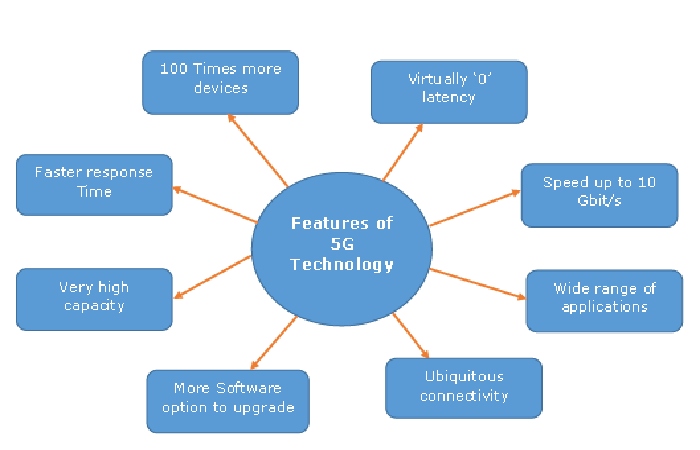
The 5G technologies are characterized by eight specifications:
- Up to 10 Gbps data speed -> 10 to 100 times better than 4G and 4.5G networks
- 1 millisecond latency
- 1000 times faster bandwidth per unit area
- Up to 100 more connected devices per unit area (compared to 4G LTE networks)
- 99.999% availability
- 100% coverage
- 90% reduction in network energy consumption
- Up to 10 years of battery life in low-power IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
Why is 5G faster?
According to communication principles, the shorter the frequency, the greater the bandwidth.
The use of shorter frequencies (millimeter waves between 30GHz and 300GHz) for 5G networks is why 5G can be faster. This high-band 5G spectrum provides the expected boost in speed and capacity, low latency, and quality.
However, the download speed of 5G can vary greatly depending on the area.
5G technology offers a meager latency rate, the delay between sending and receiving information. From 200 milliseconds for 4G, we went down to 1 millisecond (1 ms) with 5G.
A millisecond is 1/1000 of a second.
The average human reaction time to a visual stimulus is 250 ms or 1/4 of a second. People are capped at around 190-200 ms with proper training.
Imagine that your car could react 250 times faster than you.
Imagine that you could also respond to hundreds of incoming information, and you can also communicate your reactions to other vehicles and road signs, all in milliseconds.
Advantages and disadvantages of 5G technologies
As smartphone technology has advanced, customers have brought several generations of data technology to market in recent years.
People must start looking at 5G technology now to decide if the features are right for them. Against this background, what are some advantages and disadvantages of 5G technology about smartphones and other smart devices?
Advantage
As advantages of 5G technology, we highlight the following:
Higher bandwidth for all users
For those of you who don’t know, bandwidth is the amount of “space” available to people who use data to download files, view Internet pages, and watch videos. The less bandwidth is available, the slower everyone’s devices will perform.
One of the benefits of this new fifth generation of wireless technology is that there will be more bandwidth on business data networks. Many people remember 3G technology as they watched the progress bar load their web pages. In 5G, this will be a concern of the past.
As more bandwidth is available, users can also use that bandwidth to do more with their devices, making them more versatile than ever.
Faster speed
As more people can take advantage of this increased bandwidth, some people may be concerned about their speed on a 5G network. This will problem of the past as people using a 5G network can browse the internet, download files, and even stream videos at blazing speeds.
Because of the increased bandwidth, users can use more without crowding out other users. With more networks reserved for each smart device, smart devices can run faster than ever.
New technology options are available
Early research and reports on 5G technology show that intelligent devices operating on a 5G network can use a thousand times quicker than on a 4G network. With the early development of intelligent machines, tasks that in the past could only be performed on a desktop or laptop could suddenly be performed on a smart device, such as B. Email and web browsing.
With increasing network speed, more and more tasks are being shifted from the world of computers to the world of intelligent devices. As network speeds increase, this could open new doors for smart device technology that may not have been available.
Disadvantage
We can highlight the following disadvantages of 5G technology:
Less coverage
One of the main advantages of 3G cell towers was that they could cover a huge area with relatively few cells. This is because the network did not need as much bandwidth, which means the networks had fewer cells to implement.
When technology advanced to 4G networks, cells produced more bandwidth, which means that the coverage radius of each cell was smaller. People may have noticed that your coverage may drop more often than on your 3G network. As the network rolls out, this trend will continue.
More cell towers will be needed to produce this immense bandwidth because cells cannot cover as much space as a 3G or 4G cell. Because more cells will need to be deployed, Its users should expect their coverage to not be as extensive at first.
Radiofrequency can become a problem
Radios, cell phone towers, and even satellites communicate using radio frequencies. Frequency is measured in Hz, and radio frequencies tend to operate in the GHz range. Early reports on the 5G network indicate its network will transmit its data in the field of around 6 GHz.
Unfortunately, this radio frequency range is already full of other signals, such as satellite links. With many types of signals operating in the 6 GHz range, it is fair to wonder if crowding will pose a problem when people try to transmit their data signals at this frequency. Will problems be sending and receiving signals? Time will tell when this network frequency begins to spread.
